Sun-Damage & Hyperpigmentation Treatments
Offering A Variety Of Pigmentation Treatments In Oxford
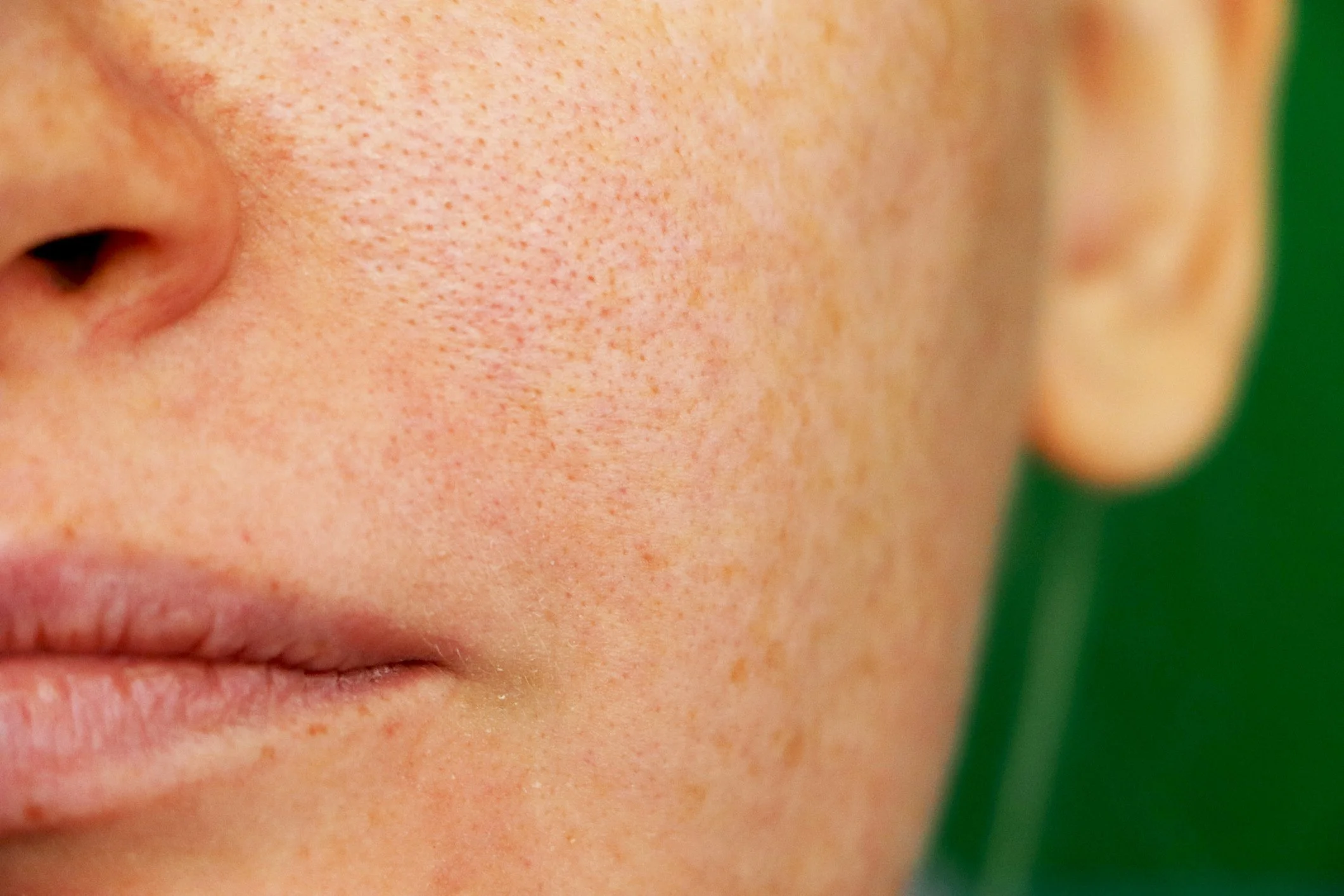
Hyperpigmentation
Before and after hyperpigmentation skin treatments at Lumiere Medispa in Oxford
What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is the blanket medical term to cover a variety of pigmentation skin disorders that affect the colour of the skin. Hyperpigmentation is usually a harmless skin condition that is characterised by the excess production of Melanin (skin pigment) from melanocyte skin cells in sporadic places of the skin, usually areas that are exposed to the sun.
What Causes Hyperpigmentation?
When the skin is exposed to the sun, a healthy skin will switch up the melanocyte melanin production to turn the skin darker and be better able to absorb harmful UV sun rays (most commonly known as a sun tan). Once the sun exposure is reduced, the melanocytes down-regulate the production of melanin and the skin cell turnover cycle expels the pigment. However, over time, excess exposure to the sun, hormonal influences and injury, can cause sporadic melanocytes to become dysfunctional and constantly up-regulate the melanin production. This results in sporadic patches of skin appearing darker than its surroundings.
Is There a Difference Between Sun-Damage Hyperpigmentation and Melasma?
Yes. Generally sun-damage induced hyperpigmentation spots (Solar Lentigines -commonly known as age spots) occur in smaller isolated patches on the skin and are relatively simple to treat without any adverse affect upon the deeper melanocyte cells. Melasma tends to be a larger and deeper collection of melanin and is more commonly associated with hormonal changes, medication, and injury. Melasma tends to be more difficult to treat and some skin treatments can make it worse, due to the deeper pigment proximity to the melanocyte and subsequent reactivity to heat or injury of any treatment.
Can all skin types Develop hyperpigmentation?
Yes white, Asian, Black and all skin types can develop hyperpigmentation because all skin types contain melanocytes. Darker skin types carry a higer percentage of melanocytes and subsequent melanin (pigment), and are more likely to develop post inflammatory hyperpigmentation (caused by injury and inflammation). Lighter skin types are more easily damaged by the sun and are more likely to develop sun-induced hyperpigmentation.
How do you treat Hyperpigmentation and Melasma?
Simple superficial hyperpigmentation, such as solar lentigines (sun damage age spots) can be treated with medical grade skin care, such as those available from our skincare shop and from AlumierMD (consultation required). Skin care, including effective daily sun protection, is the most important aspect of any hyperpigmentation treatment, however, in-clinic treatments may help to improve and speed up your results.
Treatments For Hyperpigmentation & Melasma
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL:SQ)
Our advance medical IPL device from Etherea MX effortlessly tackles superficial sun damaged skin, hyperpigmentation and sun spots. Not only will it reduce your pigmentation, it will boost your natural skin collagen content for dual benefits.
The Perfect Peel
The Perfect Peel™ is a medical medium-depth chemical peel that can be performed as a standalone treatment or in addition to another cosmetic procedure. This medical-grade peel is considered safe for all skin types and can provide beautiful results for patients of all ethnicities.
Acroma:QS
The world’s first non-ablative laser specifically created for the treatment of Melasma in all skin types.
Medical Grade Skincare
We provide a range of medical-grade at-home skincare solutions to assist you in your journey to fight hyperpigmentation.
What Next?
Talk With An Expert
Book A Consultation
We always provide a face to face consultation before any treatment. This ensures you have chosen the right treatment for your skin appearance goals.
Contact us today and book a consultation.